√画像をダウンロード universal gravitational constant and gravitational acceleration difference between 173457-Universal gravitational constant and gravitational acceleration distinguish between
The value of the universal gravitational constant is 667 × physics On the Moon, the acceleration due to gravity is 162 m/s^2 How far would a 19 g rock fall from rest in 65 seconds if the only force acting on it was the gravitational force due to the Moon?Get answer Gravitational constant and Gravitational acceleration Apne doubts clear karein ab Whatsapp par bhi Try it now0500 · Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ Write any four difference between acceleration due to gravity and universal gravitational constant rishit755 rishit755 0500

Differentiate Between Gravitational Constant And Acceleration Due To Gravitation State Laws Of Brainly In
Universal gravitational constant and gravitational acceleration distinguish between
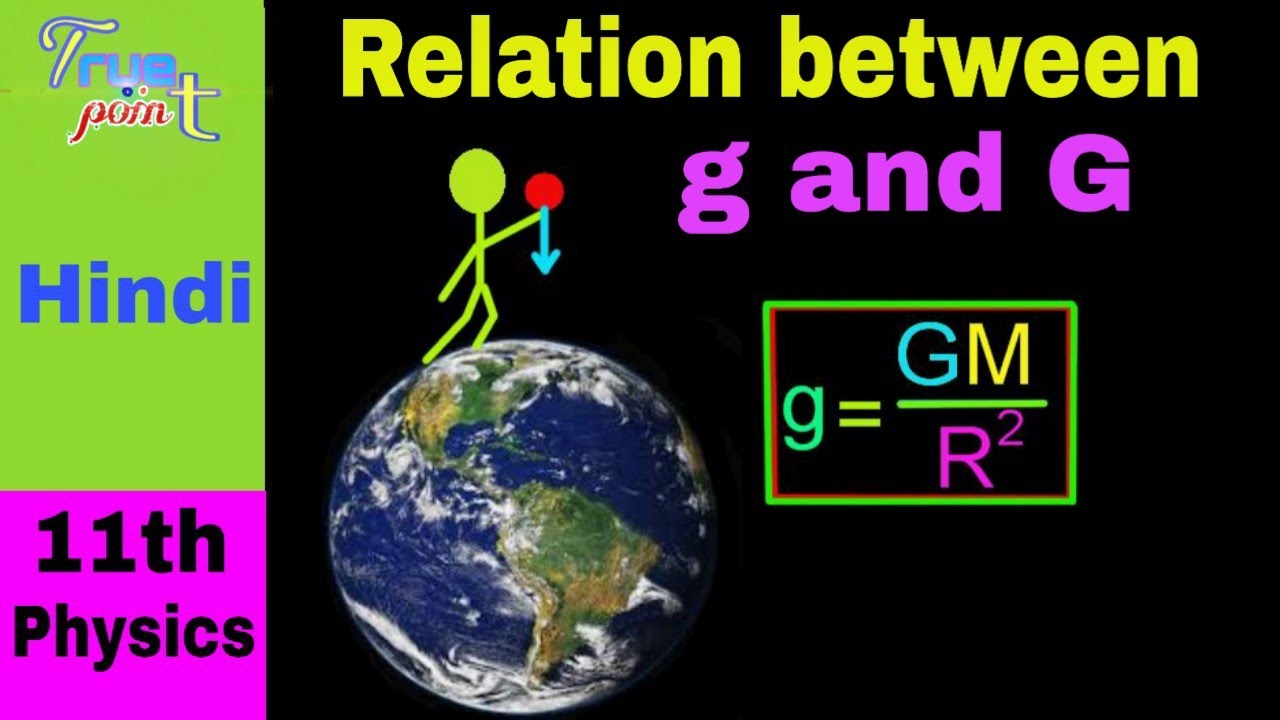
Universal gravitational constant and gravitational acceleration distinguish between-The value of the universal gravitational constant is 6673*10^ 11 Nm^ 2 /kg^ 2 Answer in Math The acceleration due to gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the centre of Earth The acceleration due to gravity for a satellite orbiting 7000 km above the centre of Earth is m/s^2In this Physics video lecture in Hindi for class 11 we explained the relation between acceleration due to gravity (g) and universal gravitational constant (G




The Gravitational Constant In Newton S Gravity Equation
Liczba wierszy 5 · The Universal gravitational constant is defined as the force of attraction between twoG is the universal gravitational constant, usually taken as 6670 × 1011 m 3 / (kg) (s 2) or 6670 × 10 −8 in centimeter–gram–second units1211 · • G stands for the universal gravitational constant, whereas g stands for the gravitational acceleration at a certain point • G is a constant throughout space and time, but g is a variable quantity
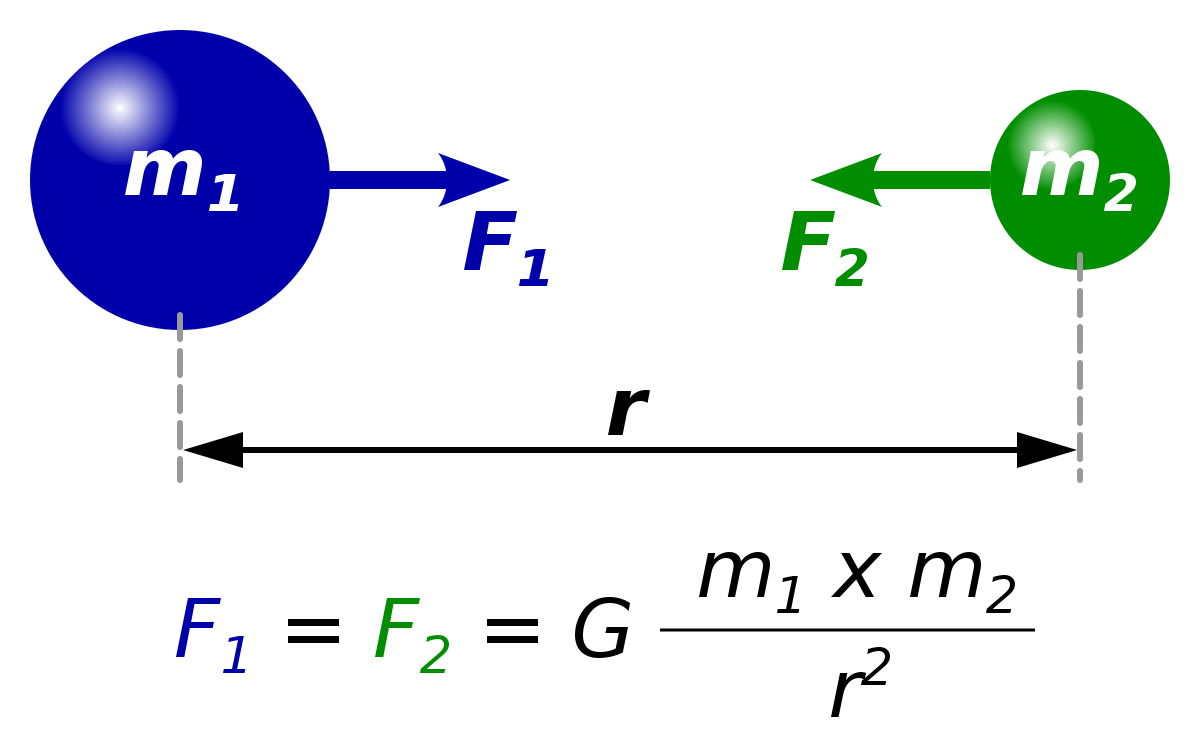
If M is the mass of the earth, G the universal gravitational constant, r the distance between the earth's center of mass and a local air parcel (consisting of a specified set of molecules) in the atmosphere, and r ^ a unit vector pointing from the earth's center toward that air parcel, then the gravitational force per unit mass exerted by the · The universal gravitation equation thus takes the form F is the gravitational force between bodies, m 1 is the mass of one of the objects, m 2 is the mass of the second object, r is the distance between the centres of two objects, G is the universal gravitational constant The value of G is 667×10 11 Nm 2 / Kg 2Correct answers 3, question Give three differences between acceleration due to gravity (Ⓡ) and universal gravitational constant (G)2
GRAVITATIONAL ACCELERATION EQUATION WITH WAVELENGTH AND SPEED OF LIGHT WITHOUT USING THE UNIVERSAL GRAVITATIONAL CONSTANT OF NEWTON Rodolfo Sergio González Castro Research Institute, University of Tijuana CUT, Av Lucrecia Toriz 1010, Col Altamira, Tijuana, Baja California, México CP Email rodolfogonzalezcastro@gmailcomThe measurement and analysis of these rates is known as gravimetry At differentGravitational Force Based on Kepler's theory of the planetary motion, Newton discovered the gravitational



Gravitational Constant Wikipedia




Equation Of Gravitational Constant And Acceleration Due To Gravity Qs Study
Gravity, Universal Gravitation Constant Gravitational Force Between Earth, Moon & Sun, Physics Gravity, Universal Gravitation Constant Gravitational Force Between Earth, Moon & Sun · The universal gravitational constant, which appears in Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation, can be used to calculate the gravitational attraction between any two masses, anywhere in the universe · (Physorg)—Newton's gravitational constant, G, has been measured about a dozen times over the last 40 years, but the results have varied by much more than would be expected due to random and




Gravity Newton S Law Of Gravity Britannica




Gravity Newton S Law Of Gravity Britannica
2501 · G is the acceleration due to gravity and its value is 98m/s2 However, this acceleration due to gravity is not a universal constant hence its value shows variation It is noteworthy that the gravitational force is extremely small in comparison to the force of gravityGravitational acceleration is that acceleration produced in an object that is experiencing gravitational force It usually varies with altitude and is not uniform anywhere While gravitational constant is the universal constant for gravitational force with which each body of universe attract every other body It's value is 6673*10^11Nm^2/kg^2Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ State Newton's law of gravitation Obtain the relation between universal gravitational constant and gravitational acceleration



Physics Project Storyboard By Kaustubh




The Basics Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Where Ppt Video Online Download
D is the distance between M1 and M2;I have read that gravitational field intensity and acceleration due to gravity are two different physical quantities that have the same direction, magnitude, and units So, if all the units, magnitudes, and directions are the same for the two quantities (and also, physically, both essentially mean the acceleration produced in a point mass at a point) then what is the difference betweenDifference Between the universal gravitation constant (G) and acceleration due to gravity (g) ANSWER The differences between G and g I as follows (1) G is called as universal gravitational constant and g is acceleration due to gravity




Differentiate Between Acceleration Due To Gravity And Universal Gravitational Constant Derive A Relation Between G



Gravity Of Earth Units Of Measurement Wiki Fandom
The formula of gravitation can be stated as F = G * (m1*m2)/R2 In this gravitational force equation F → Magnitude of the gravitational force G → It is the gravitational constant and its size depends on the system of units used m1, m2 → Masses of the two objects R Distance between the massesCorrect answers 3, question explain the difference universal gravitational constant and gravitational acceleration of the earthA constant acceleration gives us a constant mass Therefore we can plug known values for m into this equation m = Δr 3 /GΔt 2 a = 2Δr/Δt 2 a = 2mG/Δr 2 That is the acceleration of each of two equal masses in a gravitational situation But if we want to give all the acceleration to one of them, holding the other one steady for experimental



What Is The Dimension Formula For A Gravitational Constant Quora



What Are The Si Units For G The Universal Gravitational Constant Quora
In order to add the equivalent mass of kinetic energy to Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation formula it is necessary to correct its value by 2π, 2 given the double effect of the gravitational interaction of kinetic energy and π due to the character of linear acceleration in the equation above It is an issue similar to the differenceThe gravitational force acting between unit masses kept at a unit distance away from each other equals gravitational constant (G) The acceleration produced in a body under the influence of the force of gravity alone is called gravitational acceleration of earth or acceleration due to gravity (g) 2 Gravitational constant is a scalar quantity(1) G is called as universal gravitational constant and g is acceleration due to gravity (2) The value of G = × 10−11 m3 kg−1 s−2 while the value of g = 98ms−2 or10ms−2 (3) The value of G remains constant everywhere while that of g varies (4) G is a constant while g is the acceleration produced on a freely falling body



Gravitation By N Singh




Gravitation By N Singh
· The gravitational constant is the proportionality constant used in Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation, and is commonly denoted by G This is different from g, which denotes the accelerationIn physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object in free fall within a vacuum This is the steady gain in speed caused exclusively by the force of gravitational attraction At given GPS coordinates on the Earth's surface and a given altitude, all bodies accelerate in vacuum at the same rate, regardless of the masses or compositions of the bodies; · G is the universal gravitational constant, having the value of 6674 x 1011 Newton meter 2 per kilogram 2 This constant is universal, meaning that it remains a fixed value throughout the universe The gravitational field intensity, also known as gravitational acceleration, is the acceleration of any mass due to the gravitational field



Relation Between Acceleration Due To Gravity G And Universal Gravitational Constant G Youtube



1
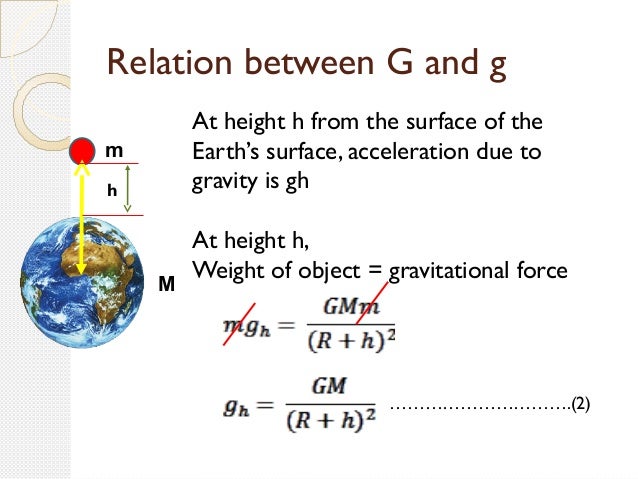
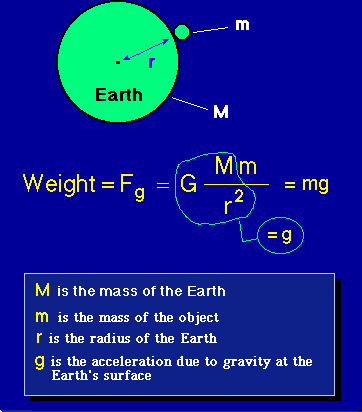
Differentiate between universal gravitational constant and acceleration due to gravity Answers 2 GetWhere g is the acceleration due to gravity, G is the universal gravitational constant, M is mass, and R is distance g = GM/R 2, since m is absent in the expression, hence acceleration due to gravity is independent of the mass of the body2 For one thing, they have different units g has units of acceleration while G has units of ( l e n g t h) 3 / m a s s / ( t i m e) 2 Physically, g really is the acceleration of a falling object Usually this is specifically for an object falling toward the Earth (and near the Earth's surface), and g ∼ 98 m / s 2




Study Guide For The Chapter 11 And Gravity Test




Introduction To Newton S Law Of Gravitation Video Khan Academy
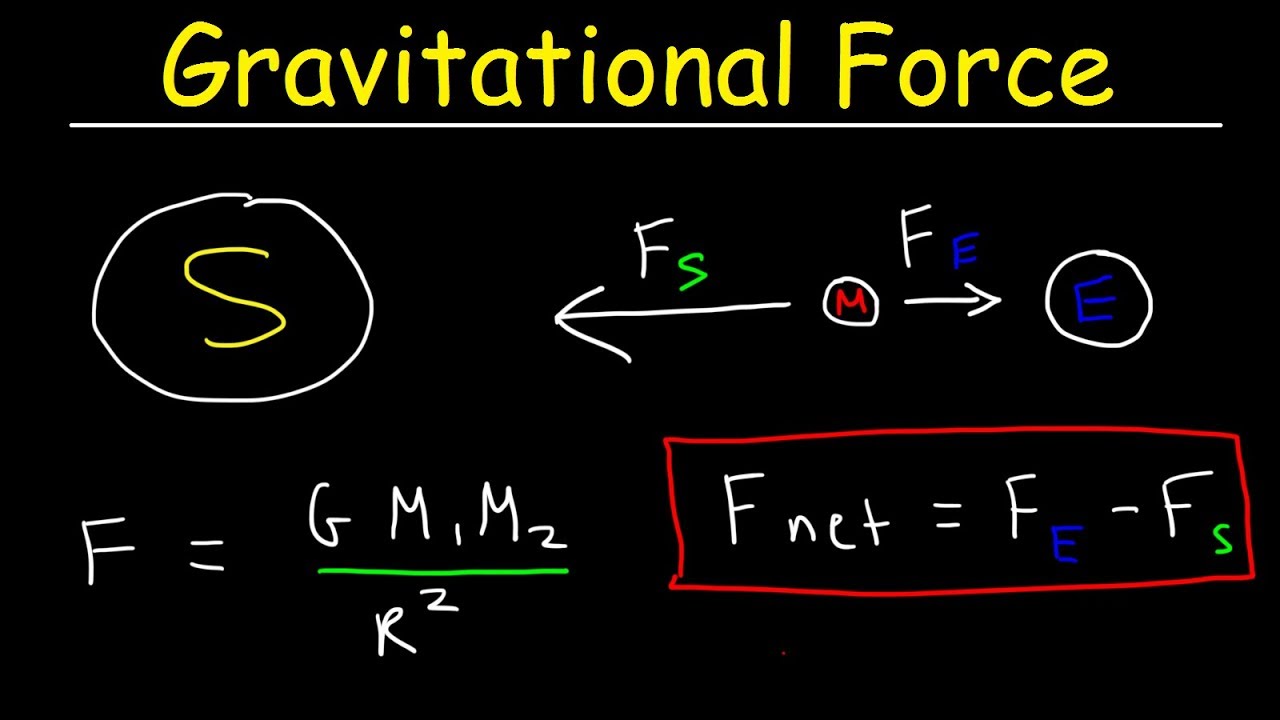
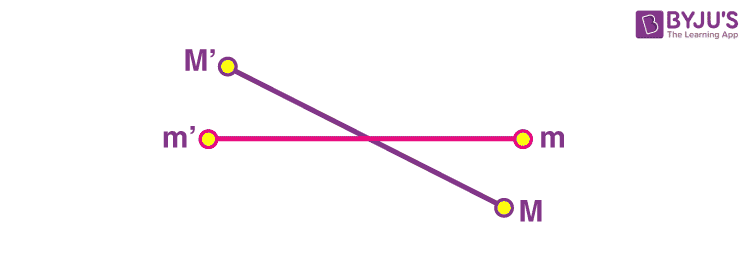
The units for G are m^3/ (kg*s^2) g is the local acceleration due to gravity between 2 objects The unit for g is m/s^2 an acceleration The 98 m/s^2 is the acceleration of an object due to gravity at sea level on earth You get this value from the Law of Universal GravitationAccording to Newton's law of gravitation, F = GM1M2 d2, where F is the gravitational force between two point masses, M1 and M2; · Gravity is ``universal'' in the sense that, in the Newtonian approximation, all masses attract each other with a force proportional to the gravitational constant, independently of the




Give Difference Between Universal Gravitational Constant G And Acceleration Due To Gravity G Brainly In




Gravity Of Earth Wikipedia
GRAVITATIONAL ACCELERATION EQUATION WITH WAVELENGTH AND SPEED OF LIGHT WITHOUT USING THE UNIVERSAL GRAVITATIONAL CONSTANT OF NEWTON Rodolfo Sergio González Castro Research Institute , University of Tijuana CUT, Av Lucr ecia Toriz 1010, Col Altamira, Tijuana, Baja California, México CP Email rodolfogonzalezcastro@gmailcomWhat is the difference between gravitational constant and acceleration due to gravity?Universal gravitation constant(G) 1It is define as the force of attraction acting between two bodies each of unit mass, whose centers are placed unit distance apart 2 Its value is same throughout the universe 3 It is a scalar quantity 4 Its value dose not depends upon the nature and the size of the bodies 5




Clic Energy Wilen Its Velocity Is Increased Three Times 3 10 Differentiate Between Acceleration Due To Gravity And Universal Gravitational Constant Derive A Relation Between G And G 3
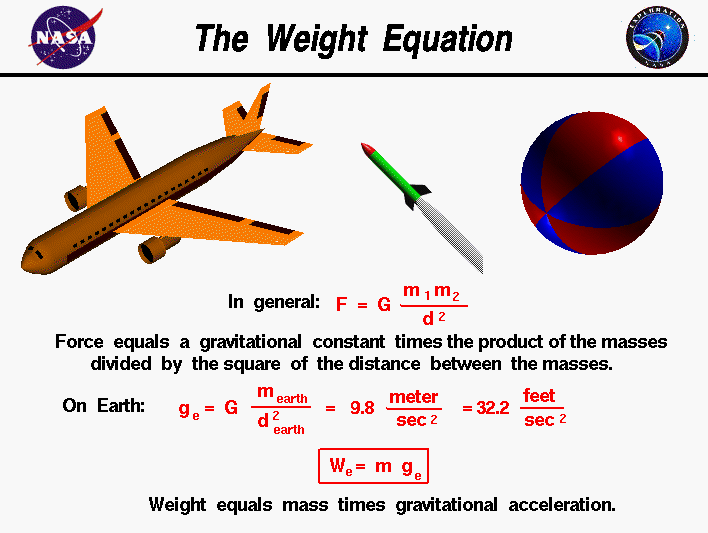



Weight Equation
Correct answer to the question Give three differences between acceleration due to gravity (Ⓡ) and universal gravitational constant (G)2 brainsanswersin · G stands for Newton's universal gravitational constant, whereas g stands for the acceleration due to gravity at a certain point G = × 1011 Nm2kg2, G is a constant throughout space and time and it is a scalar quantity g = 98 ms2, g is acceleration due to gravity which is a variable quantity and a vector qualtityPlease enter your email address You will receive a link and will create a new password via email




The Gravitational Constant In Newton S Gravity Equation




G Vs G Obviously It S Very Important To Distinguish Between G And They Are Obviously Very Different Physical Quantities G The Universal Gravitational Constant It Is The Same Everywhere In
This means that the true gravitational acceleration is 9 0339 = 9 8144 m/s 2 At the poles the Gravitational acceleration is 9 22 m/s 2 The difference between the poles and the equator is that objects on the Equator are still about 21 km away from the center of the earthAcceleration due to gravity(g) 1It is define as the constant acceleration produced in a body when it falls freely under the effect of gravity 2 its value changes from place to palce 3 it is a vector quantity 4 Its value depends upon the nature and the size of the bodies 5 Dimensional formula for g is M 0 L 1 T2G is a constant, the value of which was obtained by Henry Cavendish, whereas g is an acceleration that is involved whenever an object is falling or ascending in the earth's atmosphere Moreover, what G and g are and how these value are obtained can be understood as




Relation Between Acceleration Due To Gravity And Gravitational Constant Hindi Explanation Youtube




Law Of Gravity




What Is The Difference In Between Of G And G Please Tell Brainly In




Gravitation Part 2 Video Khan Academy
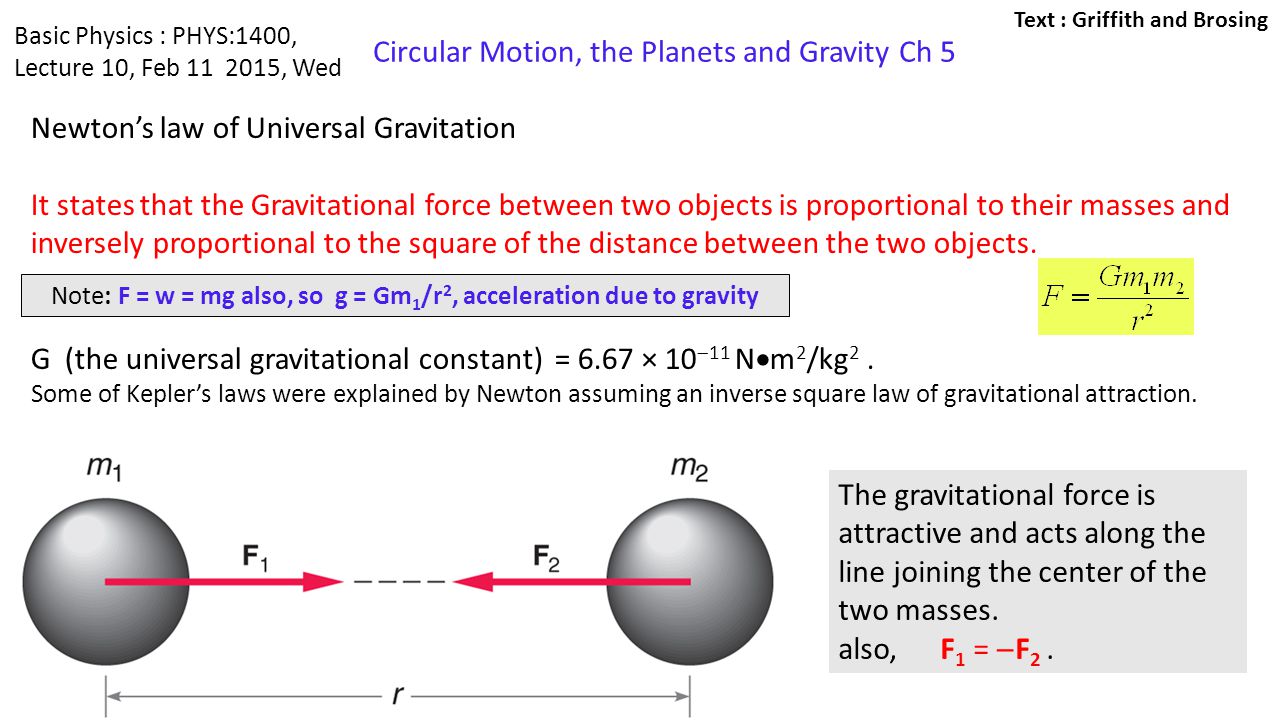



Note F W Mg Also So G Gm1 R2 Acceleration Due To Gravity Ppt Download



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation




Difference Between Gravitation And Gravity With Comparison Chart Circuit Globe




Gravitation
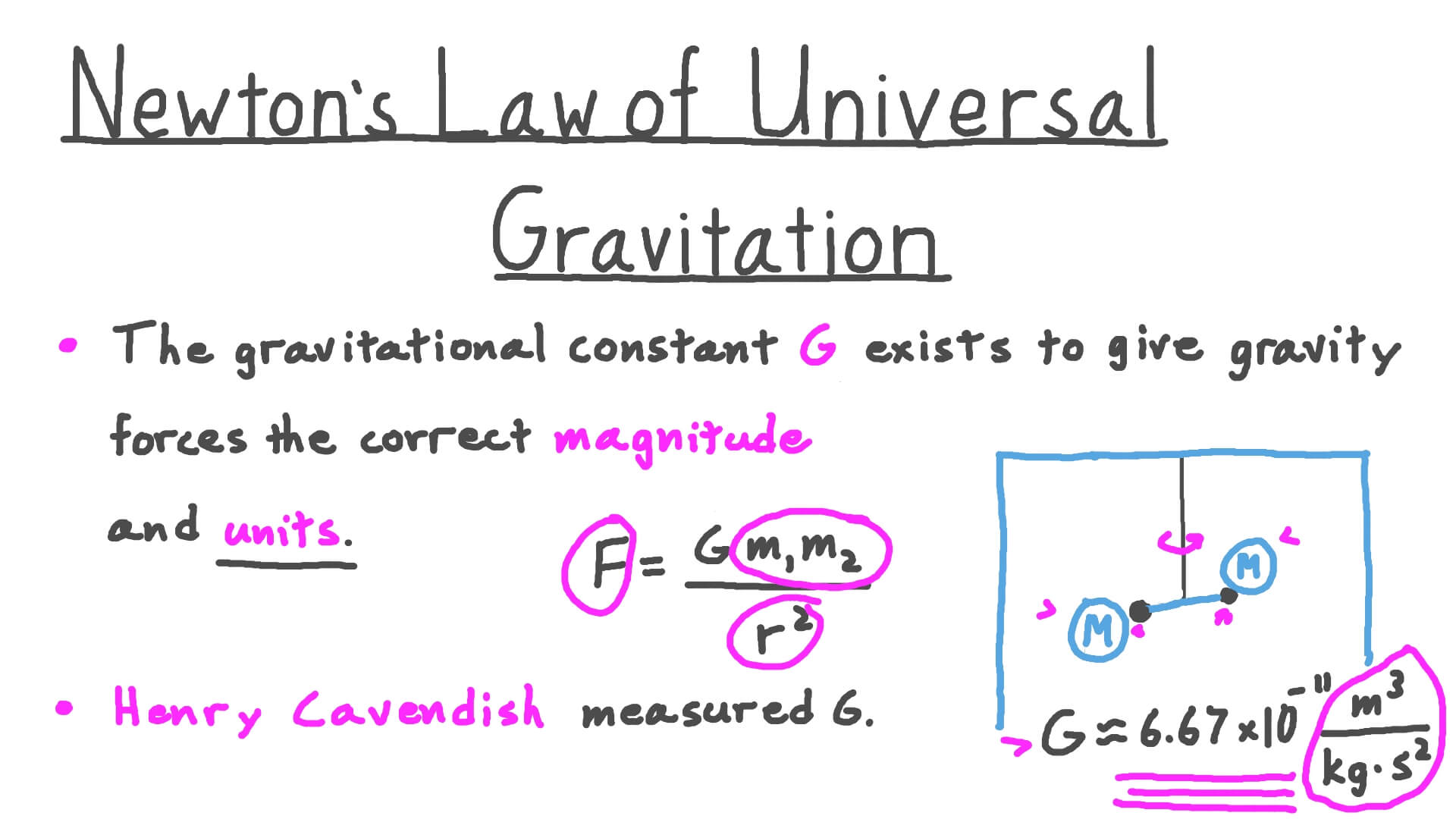



Lesson Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Nagwa



1




Question Video Finding The Distance Between The Centres Of Two Bodies Given The Gravitational Force Between Them Nagwa



Calculating Acceleration Due To Gravity Formula Concept Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Gravity Newton S Law Of Gravity Britannica




Big G Scientists Pin Down Elusive Gravitational Constant Live Science
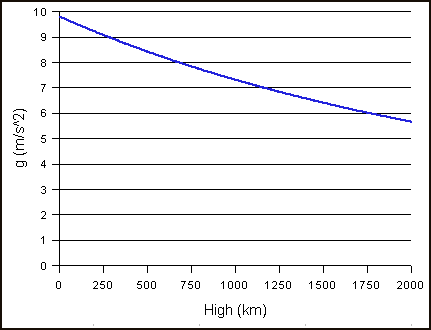



Gravity Of Earth Units Of Measurement Wiki Fandom




Halliday Resnick Walker Fundamentals Of Physics 8th Edition Ppt Video Online Download
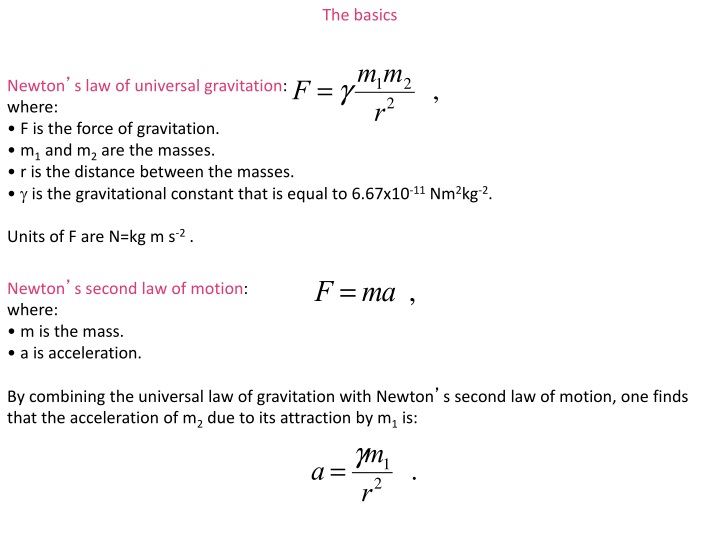



Ppt Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Where F Is The Force Of Gravitation Powerpoint Presentation Id




The Law Of Universal Gravitation Definition Importance Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Abbreviations Symbols And Units G Universal Gravitational Constant Download Scientific Diagram
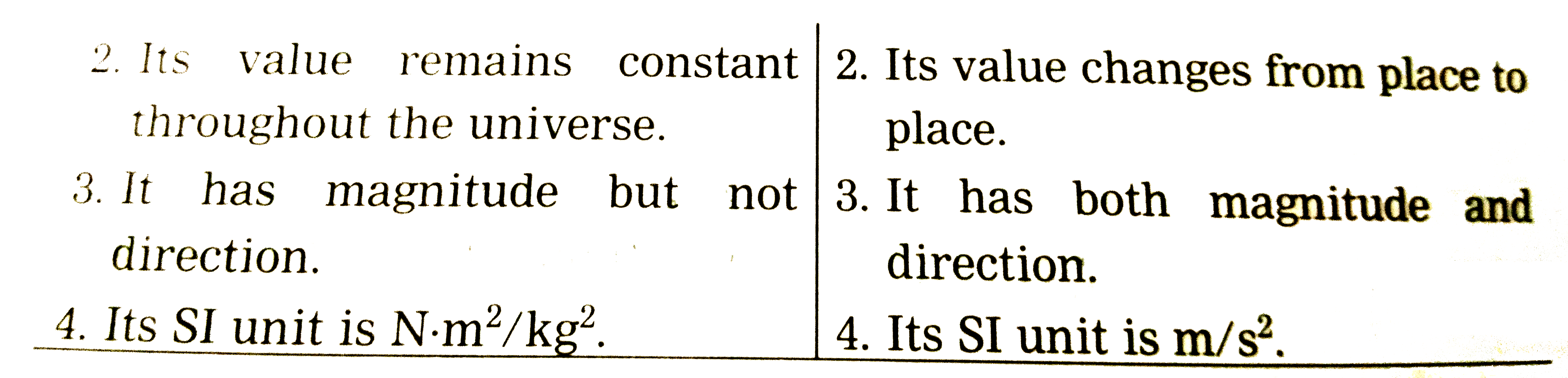



Universal Gravitational Constant And Gravitational Acceleration Of




Newtons Universal Law Of Gravitation This Cartoon Mixes




Differentiate Between Gravitational Constant And Acceleration Due To Gravitation State Laws Of Brainly In




Solved A Explain The Relationship Between The Universal Chegg Com




If G Is Universal Gravitational Constant And G Is Acceleration Due To Gravity Then The Youtube



1



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation




The Gravitational Constant In Newton S Gravity Equation




To Find The Gravitational Acceleration G On The Chegg Com



1
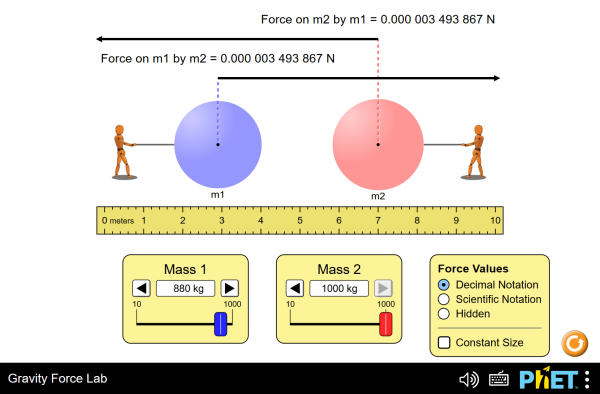



Gravity Force Lab




Acceleration Due To Gravity At The Space Station Video Khan Academy
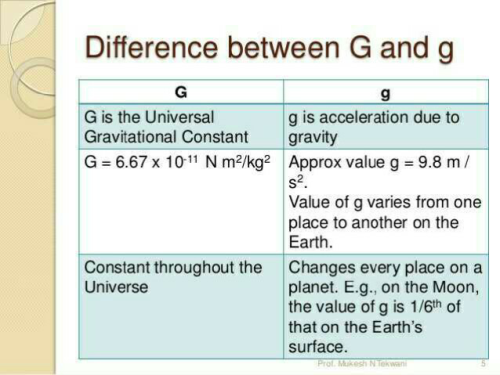



What Is The Difference Between G And G Edurev Neet Question




What Are The Differences And Similarities Between Acceleration Due To Gravity G And Universal Gravitational Constant G Quora




Gravitational Force Flip Ebook Pages 1 35 Anyflip Anyflip




Difference Between G Universal Gravitational Constant And G Acceleration Due To Gravity By Vandana Rajput A Podcast On Anchor




Universal Gravitational Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Http Mrdclassified Weebly Com Uploads 1 3 5 0 Ugwkst1 Pdf
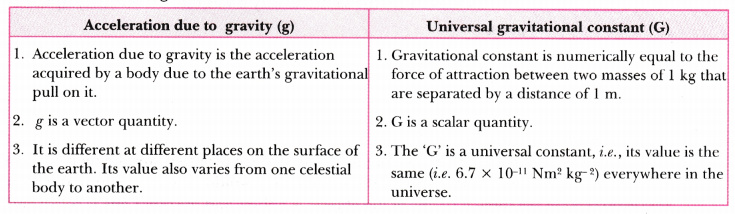



Give Three Differences Between Acceleration Due To Gravity G And Universal Gravitational Constant G Cbse Class 9 Science Learn Cbse Forum




What Are The Differences And Similarities Between Acceleration Due To Gravity G And Universal Gravitational Constant G Quora



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Boundless Physics




Difference Between G And G Scholr




Gravitational Constant Wikipedia




Differentiate Between Acceleration Due To Gravity And Universal Gravitational Constant Derive Brainly In




Difference Between Universal Gravitational Constant And Gravitation Acceleration Of Earth
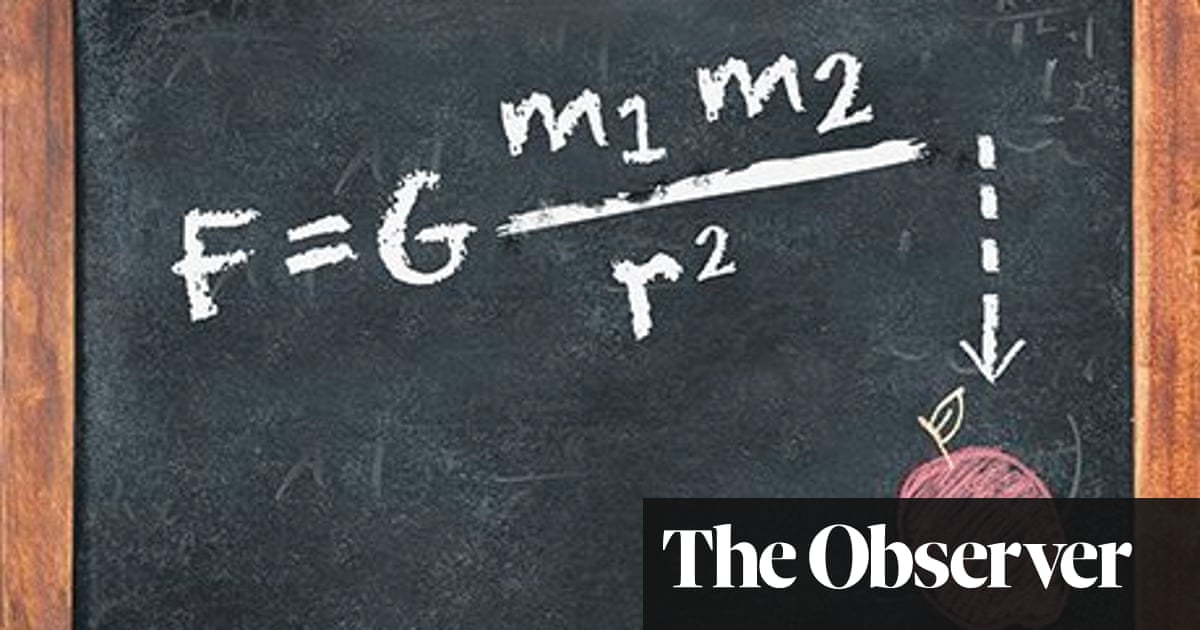



Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Isaac Newton The Guardian




Why Do Measurements Of The Gravitational Constant Vary So Much
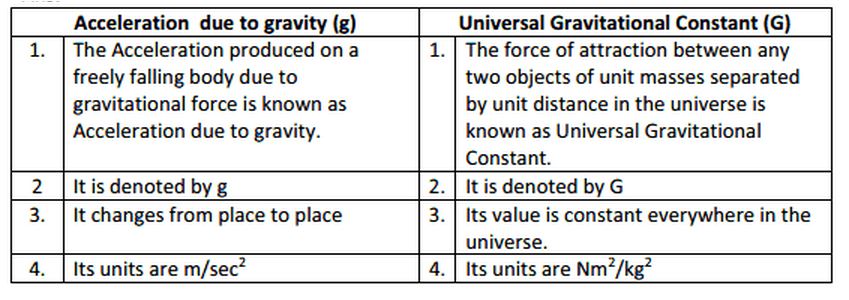



What Is Difference Between G And G Gravitation Science Class 9




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 3 Gravitation Free Pdf




7 2 Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation And Einstein S Theory Of General Relativity Texas Gateway




Two New Ways To Measure The Gravitational Constant




Mastering Physics Solutions Chapter 12 Gravity A Plus Topper




Theory Of Gravity Energy Wave The Origin By Rodolfo Sergio Gonzalez Castro Issuu




M I First Name Acceleration Due To Gravity G Chegg Com



The Most Accurate Value Of Gravitational Constant G Till Date




What Is The Gravitational Constant Universe Today



Sir Isaac Newton The Universal Law Of Gravitation



Gravity Applications



Gravity Universal Gravitation Constant Gravitational Force Between Earth Moon Sun Physics Youtube



Gravity




Swift Learning Center




Solved Acceleration Due To Gravity G 9 8 M S Universal Gr Chegg Com




Universal Gravitational Constant And Gravitational Acceleration Of




Plain Balanced And Unbalanced Force With Example Give The Difference Between Universal Gravitation Constant G And Gravitational Acceleration G A Mit Buye Fow Grams Of Gold At The Noles As Per The



Aerospaceweb Org Ask Us Gravity On Other Planets




What Is Difference Between G And G Brainly In




Pdf Precise Ideal Value Of The Universal Gravitational Constant G




What Is The Si Unit Of G And G Teachoo Extra Questions




Calculating Acceleration Due To Gravity Formula Concept Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



What Is Difference Between G And G



Hal Archives Ouvertes Fr Hal Document




Comparison Of Acceleration Due To Gravity And Universal Gravitational Constant Youtube




Gravitational Constant Wikipedia



Law Of Gravity



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation




Acceleration Due To Gravity Questions And Answers Toppr




The Acceleration Due To Gravity On The Surface Of A Planet Which Has Both Mass And Radius Half Of Those Of The Earth Is



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation




What Is Difference Between G And G




Acceleration Due To Gravity G Vs Universal Gravitational Constant G Youtube



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Gravitation Equation Universality Of Gravity




Give Three Differences Between Acceleration Due To Gravity G And Universal Gravitational Constant G Snapsolve




Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Physics


コメント
コメントを投稿